RePair develops technologies to remove lake sediment packed with nutrients in a gentle manner and transform the sediment into:
- Clean water which is led back into the lake;
- A concentrated phosphate fertilizer which can be used in food production;
- A biological carbon product for soil improvement.
The process aims to be circular, producing only potential heavy metal leftovers that can be separated and contained safely, away from the natural environment.
Behind the project are four Danish universities and Dansk Ingeniør Service (DIS, Danish Engineering Service) to develop the process, covering the following elements (illustrated below):
- Gentle extraction of sediment;
- Dehydration of sediment via for instance:
- Flocculation (def.) with bio polymers (avoiding synthetic micro or nano plastic) followed by mechanical or electro osmotic dehydration;
- Hydrothermic dehydration and carbonization (HTC) of sediment to increasethe amount of dry matter and thus the potential soil improvement;
- Extraction of phosphorus (P) and nitrogen (N) from the residual water through electrochemical processes (electrodialysis and capacitive de-ionization);
- Elektrodialytic cleaning of sediment from phosphorus (P) and potential heavy metals;
- Testing the usefulness of the various products and their qualities as fertilizers in lab and field research.
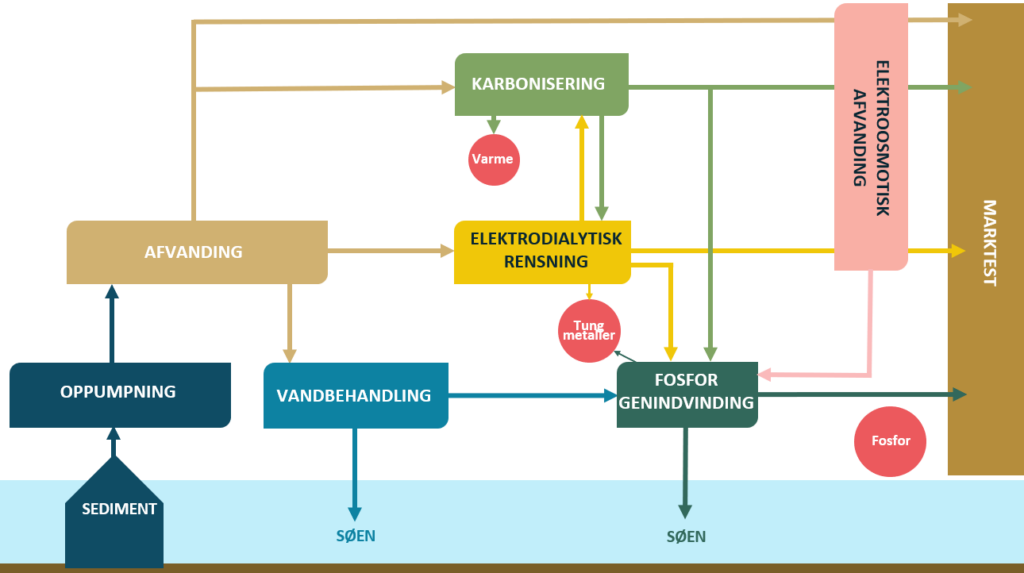
The diagram illustrates the process which cleans up the lake. Sediment is pumped and dehydrated. There are three possible paths for the dry matter 1) further dehydration, 2) carbonization, or elektrodialytical cleaning. Residue water is led back into the lake or further treated before to recover dissolved phosphorus. Illustration: Janne Jørgensen/Grundfos Foundation
Lake Ormstrup is our model lake, but the aim of the project is to provide results and experience to expand resource recovery to many more lakes with various degrees of pollution. Besides providing a toolbox for circular lake repair, each individual work package will contribute to the scientific pool of knowledge within soil physics and colloid chemistry, transport of substances and ions in electrical fields, carbonization and the impact of microplastic on plant growth.
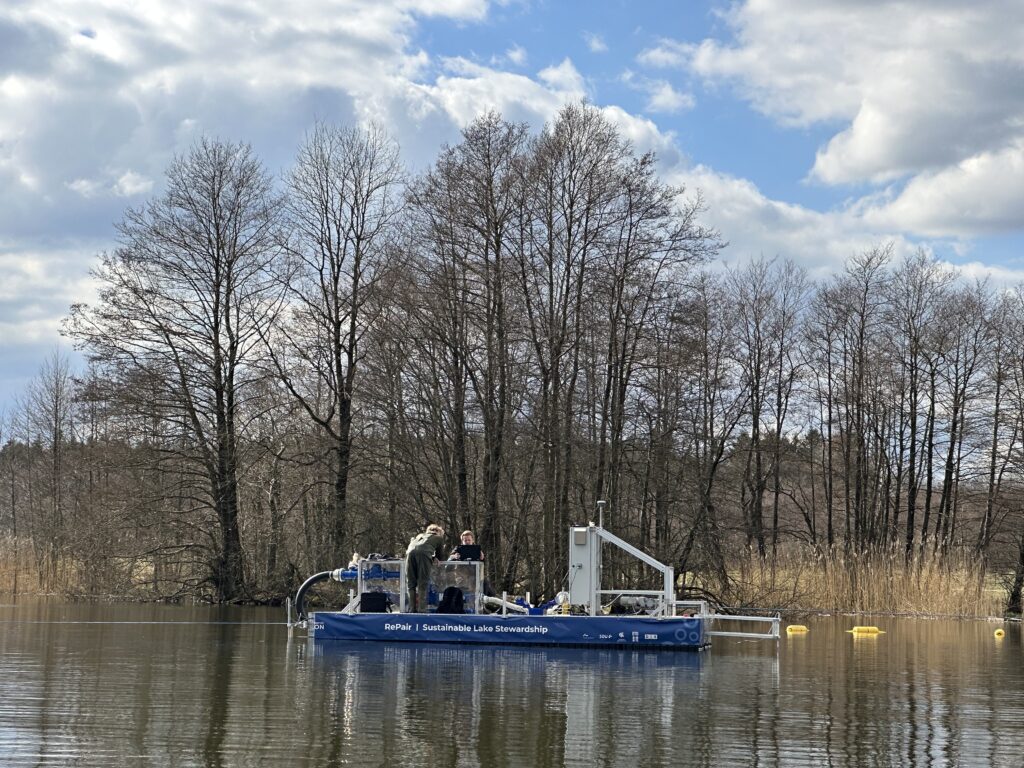

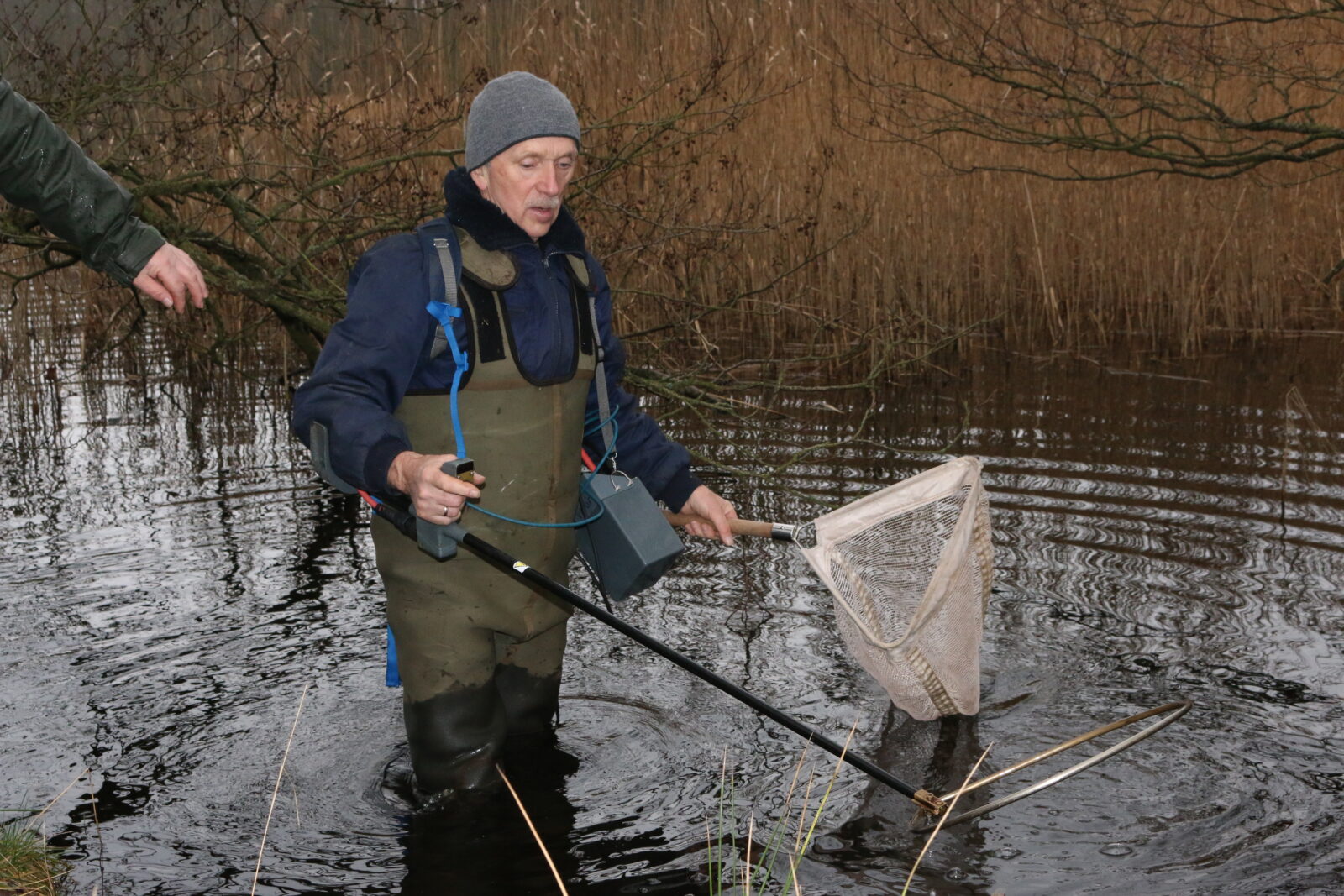
The floating platform removes sediment from the lake which is then dehydrated and tested for various purposes. Photo: Steffen Buck-Hansen, DIS
The scientific contributions will improve the use of advanced technology for lake restoration and hopefully also impact other uses of the individual treatment technologies. In short, we want to change the existing paradigms in lake restoration and make it possible to include lake restauration and resource recovery in the same process.
The project has been defined by the Grundfos Foundation and includes four universities:
- AAU Department of Chemistry and Bioscience, Assistant Professors Morten Lykkegaard Christensen and Jens Muff
- SDU Department of Biology, Assistant Professor Kasper Reitzel
- DTU Department of Civil and Mechanical Engineering, Professor Lisbeth M. Ottosen
- AU Department of Biological and Chemical Engineering, ledet af Postdoc Aidan Mark Smith
The project runs parallel to “Sustainable Lake Stewardship”.